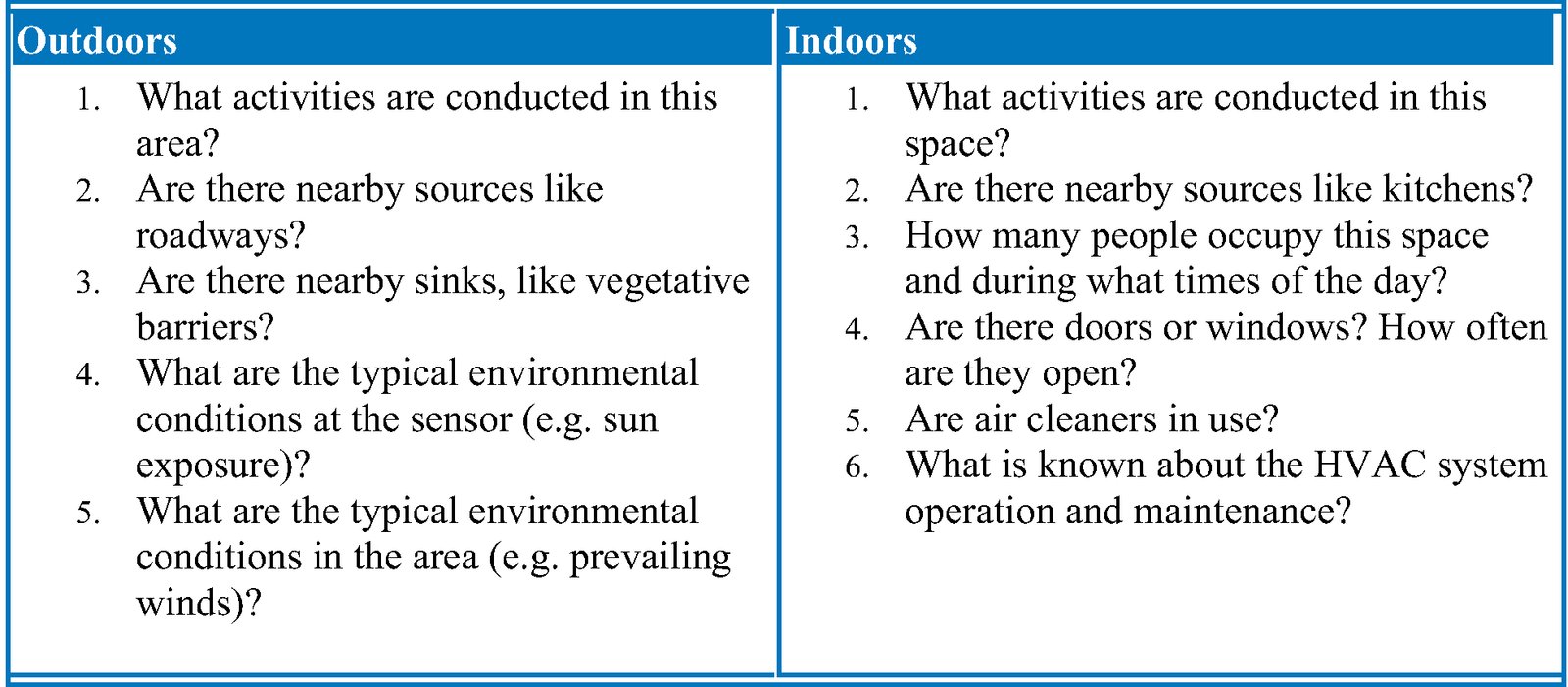
Indoor air pollution originates from sources within the building, such as furniture and paints, while outdoor air pollution comes from external sources like factories and vehicles, spreading through the atmosphere. Indoor air pollution is caused by materials within the building, while outdoor air pollution comes from external sources that emit pollutants into the atmosphere.
Understanding the distinctions between these two types of pollution is crucial for addressing their effects on human health and the environment. Let’s explore further how indoor and outdoor air pollution impact the population and what measures can be taken to mitigate their harmful effects.
Understanding Indoor Air Pollution
Indoor air pollution refers to contaminants that come from objects or materials within a building, such as furniture and paints, which often remain within the building. On the other hand, outdoor air pollution refers to emissions from sources outside the building, like factories, cars, and wildfires, which can spread throughout the atmosphere.
| Definition of indoor air pollution: Indoor air pollution refers to contamination of air within enclosed spaces, such as homes and buildings. This pollution can be caused by various sources including furniture, construction materials, and activities like cooking. |
| Sources of indoor air pollution: Common sources of indoor air pollution include burning fuel for cooking and heating, emissions from furniture and construction materials, and activities like smoking. These pollutants can have adverse effects on human health if not properly addressed. |
Understanding Outdoor Air Pollution
Outdoor air pollution is derived from external sources such as factories and vehicles, while indoor pollution originates from within enclosed spaces like cooking and heating. By understanding these distinctions, we grasp the varied impacts on health and the environment.
| Definition of outdoor air pollution: Refers to emissions from factories, cars, fires, pesticides. |
| Sources of outdoor air pollution: Burning of fossil fuels, industrial activities. |
Key Differences Between Indoor And Outdoor Air Pollution
Indoor air pollution stems from furniture and construction materials, while outdoor pollution originates from factories and vehicles, spreading freely in the atmosphere. The pollutants vary, affecting human health differently in both environments.
| Key Differences between Indoor and Outdoor Air Pollution |
|---|
|

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Health Impacts Of Indoor And Outdoor Air Pollution
Indoor air pollution mainly consists of contaminants from furniture, paints, and adhesives, which remain within the building. On the other hand, outdoor air pollution refers to emissions from factories, cars, fires, and pesticides, spreading throughout the atmosphere. The health impacts of indoor and outdoor air pollution include respiratory infections, heart disease, lung cancer, and a significant impact on asthmatics.
Mitigation And Prevention Strategies
Indoor air pollution typically originates from sources within the building, such as furniture and paints, and can persist within the indoor environment. On the other hand, outdoor air pollution emanates from external sources like factories, vehicles, and wildfires, dispersing freely throughout the atmosphere. Improving indoor air quality involves addressing the emissions from furniture, adhesives, and household products, while reducing outdoor air pollution requires measures to mitigate emissions from industrial activities, transportation, and agriculture. Effective mitigation and prevention strategies for both types of pollution are crucial for safeguarding human health and the environment.
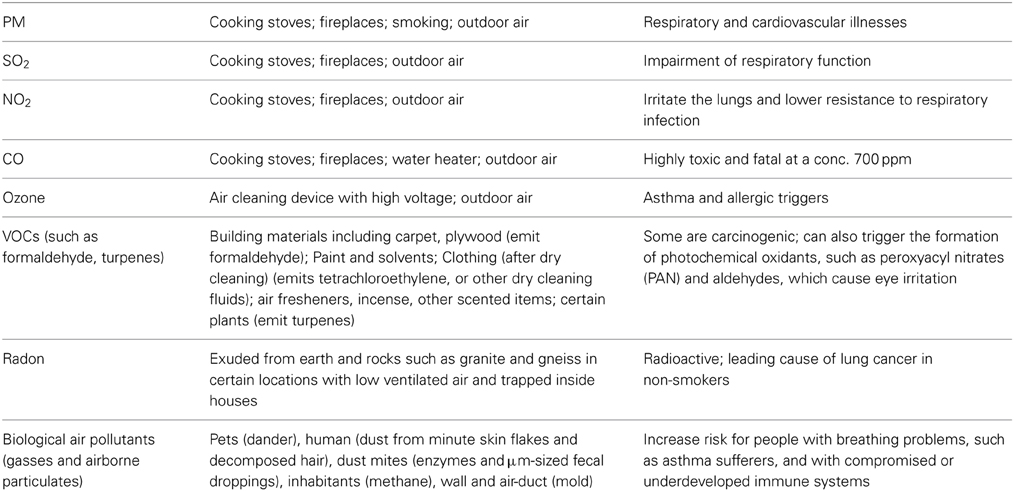
Credit: www.frontiersin.org

Credit: slideplayer.com
Frequently Asked Questions Of What Is The Difference Between Indoor And Outdoor Air Pollution?
What Is Difference Between Indoor And Outdoor Air Pollution?
Indoor air pollution comes from sources within a building, like furniture and construction materials, and usually stays inside. Outdoor air pollution comes from external sources like factories, cars, and fires, and spreads throughout the atmosphere.
Is Air Pollution Worse Inside Or Outside?
Air pollution is generally worse indoors, with pollutants from furniture, paints, and adhesives lingering inside buildings. Outdoor pollution comes from sources like factories and cars, freely spreading throughout the atmosphere.
Is Indoor Air Typically More Polluted Than Outdoor Air?
Yes, indoor air is typically more polluted than outdoor air due to contaminants from furniture, paints, and adhesives staying within the building. Outdoor air pollution comes from emissions from nearby factories, cars, fires, and pesticides, spreading throughout the atmosphere. Hence, indoor air pollution is usually more concentrated and harmful.
What Is The Outdoor Air Pollution?
Outdoor air pollution refers to the presence of pollutants in the air outside of enclosed spaces. These pollutants can come from sources such as factories, cars, fires, and pesticides. They are free to spread throughout the atmosphere.
Conclusion
Indoor and outdoor air pollution have distinct differences. Indoor air pollution originates from objects and materials within the building and can be caused by factors such as cooking, burning fuel, and construction materials. On the other hand, outdoor air pollution comes from external sources like factories, vehicles, fires, and agricultural activities.
Both types of pollution have detrimental effects on human health and can lead to respiratory infections, heart disease, lung cancer, and asthma. Understanding the differences between indoor and outdoor air pollution is crucial for creating effective strategies to reduce pollution and safeguard our well-being.
Rakib Sarwar is a Registered Pharmacist and a reputed health and wellness blogger. He has a great interest in Air purifiers.